Upstage AI Lab 2기
2024년 3월 5일 (화) Day_057
온라인강의
torch.rand()
torch.randn()
torch.randint()
torch.zeros()
torch.ones()
torch.full()
torch.eye()
| 텐서 조작(1) | 0:52:50 |
03/05 (화)
|
2:10:27
|
| 텐서 조작(2) | 0:34:17 |
Tensor Manipulation
텐서 생성
torch.rand() - uniform distribution
torch.randn() - Gaussian distribution
-> 원하는 텐서의 크기만큼 size(int) 를 차례대로 넣어주면 됨
예)
torch.rand(5, 3, 2)
tensor([[[0.7058, 0.4746],
[0.7122, 0.3221],
[0.5590, 0.6562]],
[[0.3954, 0.7389],
[0.9815, 0.1551],
[0.4234, 0.7967]],
[[0.7965, 0.5173],
[0.6794, 0.9939],
[0.9677, 0.9262]],
[[0.4459, 0.4924],
[0.1714, 0.9617],
[0.6417, 0.4669]],
[[0.3698, 0.9386],
[0.1353, 0.3009],
[0.0227, 0.5080]]])
torch.randint(low, high, (size)) - 정수 범위 내에서 랜덤 추출 (범위 : low 포함, high 미포함)
예)
torch.randint(1, 10, (5, 5, 5))
tensor([[[3, 1, 9, 2, 4],
[1, 7, 8, 4, 8],
[3, 7, 1, 5, 3],
[4, 1, 1, 5, 9],
[1, 8, 2, 6, 2]],
[[5, 7, 8, 7, 2],
[6, 7, 1, 5, 3],
[8, 4, 2, 2, 4],
[2, 5, 2, 7, 8],
[5, 9, 2, 7, 3]],
[[3, 6, 2, 7, 8],
[6, 2, 4, 4, 2],
[4, 8, 8, 3, 3],
[7, 4, 9, 5, 1],
[8, 5, 8, 7, 4]],
[[2, 8, 5, 1, 5],
[6, 7, 7, 5, 6],
[8, 1, 8, 6, 7],
[6, 4, 1, 7, 7],
[1, 1, 7, 1, 4]],
[[1, 6, 5, 3, 2],
[4, 7, 3, 8, 6],
[3, 6, 4, 1, 9],
[8, 8, 2, 6, 2],
[7, 4, 6, 9, 3]]])
torch.zeros(size) - 모든 요소가 0인 tensor
torch.ones(size) - 모든 요소가 1인 tensor
예)
torch.zeros(3, 3, 3)
tensor([[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]]])
torch.full((size), val) - 모든 요소가 지정된 값으로 채워진 tensor
torch.eye(n) - n*n 단위행렬
텐서로 변환
torch.tensor()
list, tuple, numpy array 등을 tensor로 변환 가능
numpy array 를 tensor로 변환하는 또 다른 방법
torch.from_numpy()
torch.as_tensor() - data와 메모리 공유
print('torch.tensor()')
data1 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
tensor1 = torch.tensor(data1)
data1[0] = 10
print(tensor1)
torch.tensor()
tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(data1)
[10 2 3 4 5]
print('torch.as_tensor()')
data2 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
tensor2 = torch.as_tensor(data2)
data2[0] = 10
print(tensor2)
torch.as_tensor()
tensor([10, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(data2)
[10 2 3 4 5]
torch.tensor
tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
----------------------------------------------------------------------
torch.as_tensor
tensor([10, 2, 3, 4, 5])
torch.tensor()와 torch.Tensor()의 차이!
torch.tensor() -> 원본 dtype을 따라감
torch.Tensor() -> float32 type tensor
torch.tensor(data, dtype=torch.float32)
torch.index_select
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.index_select.html
my_index = torch.tensor([0, 2])
# 선택하고자 하는 index 는 텐서 형태이어야 함.
torch.index_select(tmp_2dim, dim=1, index=my_index) # 열을 기준으로 0열과 2열을 추출
note : 출력되는 tensor의 ) 앞 ] 갯수로 차원 알 수 있음
torch.masked_select
torch.masked_select(tmp_2dim, mask = mask)
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.masked_select.html
torch.take
torch.take(tmp_2dim, index = my_index)
# Tensor가 1차원으로 flatten했을 때 index 번호로 접근
torch.gather
torch.gather()
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.gather.html
주어진 차원 내에서 인덱스로 접근?
tensor(l, m, n) n → 열, m → 행, l → 채널, dim=0은 행, dim=1은 열, dim=2는 채널???
tmp_2dim = torch.tensor([[i for i in range(10)],[i for i in range(10,20)]])
recon_index = torch.tensor([[0 ,1],[9, 8]])
torch.gather(tmp_2dim, dim = 1, index = recon_index)
tensor([[ 0, 1],
[19, 18]])
정확히는 이해 못 했음. 나중에 다시 체크하기
tensor shape 확인
.size()
.shape
tensor shape 변경
1) .reshape()
.view() 도 reshape()과 동일한 역할을 함
???????????
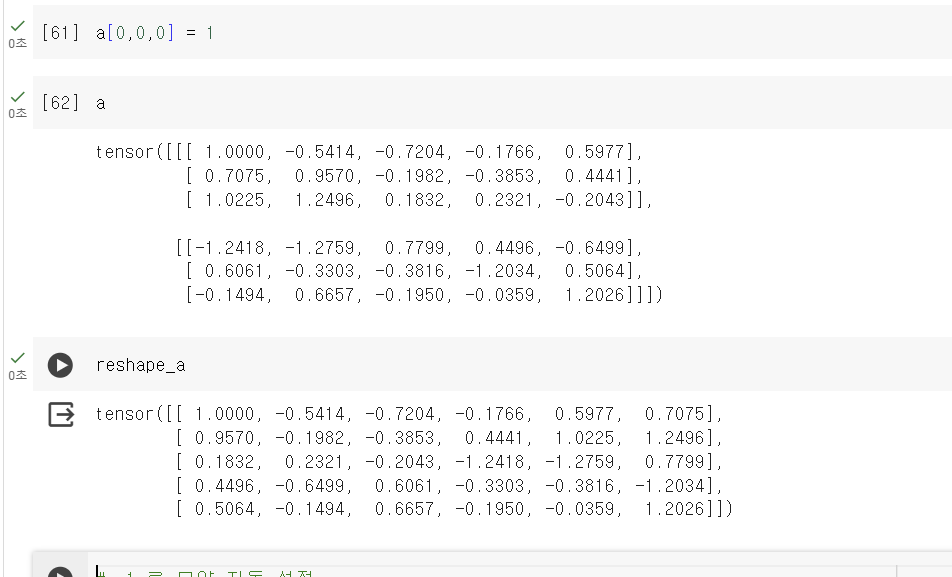
메모리 공유가 안되는 거면, reshape_a의 결과는 변하면 안되는것 아닌가??????????
reshape 전 후 원소의 갯수는 같아야 함.
.reshape( , -1) 나머지 크기는 자동 조절


2) .transpose(dim0, dim1) - dim0, dim1 를 transpose 해줌
예)
Shape : torch.Size([3, 2, 5])
↓
trans_a = tensor_a.transpose(1, 2)
↓
Shape : torch.Size([3, 5, 2])
3) .permute()
.transpose()와 유사함
4) .unsqueeze()
5) .squeeze()
6) .expand()
1차원 텐서 : (m,) -> (x,m)
2차원 이상 : 크기가 1인 차원에 대해서만 적용 가능
7) .repeat(i, j)
(m,n) -> (m*i, n*j)
8) .flatten()
start_dim로 flatten을 시작할 차원 지정 가능, default는 start_dim=0
9) .ravel()
.flatten() 과 유사하지만 평탄화의 기준이 될 축을 지정할 수 없음

역할이 비슷한 함수들
.view() / .reshape() / .unsqueeze()
contiguous : 메모리 상에서의 연속성
.is_contiguous() 함수로 확인 가능
.view() : contiguous 하지 않은 텐서에 대해 작동하지 않음
.reshape() : contiguous 하지 않은 텐서도 contiguous하게 만든 뒤 reshape
.unsqueeze() : 차원의 크기가 1이 아니면 변경 불가
.transpose() / .permute()
.transpose() : 인자 2개
.permute() : 인자 개수 = 차원의 개수


41:23부터 다시 듣기
'Upstage AI Lab 2기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Upstage AI Lab 2기 [Day058] 수강생 TODO #01 - MNIST CNN (0) | 2024.03.06 |
|---|---|
| Upstage AI Lab 2기 [Day058] CNN 구현 (0) | 2024.03.06 |
| Upstage AI Lab 2기 [Day057] PyTorch (0) | 2024.03.05 |
| Upstage AI Lab 2기 [Day057] CH.4 - CNN, RNN, From AlexNet to ChatGPT (2) | 2024.03.05 |
| Upstage AI Lab 2기 [Day055] Deep Learning - 성능고도화 (0) | 2024.03.04 |



